Friday, December 11, 2015
Enable Internet Access to Virtual Box (Oracle VM)
- Open Oracle VM Virtualbox Manager
- Right Click on Settings of the VM you want to enable
- Click on the Network tab, Enable Network Adapter
- Attached to Bridge Adapter and choose the Name of your internet adapter. Refer the screenshots below
- Then, start the VM and using root, enter the command ifup eth0 to enable the network interface of the VM. (more details see the link http://www.computerhope.com/unix/ifup.htm)
Install CentOS 6 on Oracle VM (Virtual Box)
Initial Software requirements:
Download Link: http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/server-storage/virtualbox/downloads/index.html
CentOS 6.4 minimal iso file
Download link: https://wiki.centos.org/Download
Choose CentOS Linux version 6 and download the x86_64 iso image.
Lets Begin the installation process:
- Open Oracle VM Virtualbox, and click New.
- Choose Default parameters until you see the final screen. (refer below screenshots)
- Start the VM with the CentOS 6.4 iso file
- Choose defaults and you will asked to enter Country, timezone and root password details
- Voila!!! your VM is ready with CentOS 6.4 Linux version.
Below are the above steps in details with screenshots:
Monday, October 5, 2015
Monday, September 21, 2015
RMAN-06059: expected archived log not found and ORA-19625
Problem:
RMAN-03002: failure of backup command at 03/04/2013 08:00:23
RMAN-06059: expected archived log not found, lost of archived log compromises recoverability
ORA-19625: error identifying file /opt/oracle/archredo0/foprod1/1_49507_765747965.arc
ORA-27037: unable to obtain file status
Solution:
1. Login rman
fodbsx7.hk.ocean.local:/opt/oracle/archredo0/foprod1$ so -a -s foprod1 rman target /
2. Run crosscheck copy
RMAN> crosscheck copy;
released channel: ORA_DISK_1
allocated channel: ORA_DISK_1
channel ORA_DISK_1: sid=263 devtype=DISK
validation failed for archived log
archive log filename=/opt/oracle/archredo0/foprod1/1_49507_765747965.arc recid=67567 stamp=809109558
validation failed for archived log
archive log filename=/opt/oracle/archredo0/foprod1/1_49508_765747965.arc recid=67568 stamp=809109559
validation failed for archived log
archive log filename=/opt/oracle/archredo0/foprod1/1_49509_765747965.arc recid=67569 stamp=809109560
validation failed for archived log
archive log filename=/opt/oracle/archredo0/foprod1/1_49510_765747965.arc recid=67570 stamp=809109562
validation failed for archived log
archive log filename=/opt/oracle/archredo0/foprod1/1_49511_765747965.arc recid=67571 stamp=809109564
validation failed for archived log
3. Delete expired copy;
RMAN> delete expired copy;
released channel: ORA_DISK_1
allocated channel: ORA_DISK_1
channel ORA_DISK_1: sid=263 devtype=DISK
List of Archived Log Copies
Key Thrd Seq S Low Time Name
------- ---- ------- - --------- ----
67567 1 49507 X 02-MAR-13 /opt/oracle/archredo0/foprod1/1_49507_765747965.arc
67568 1 49508 X 02-MAR-13 /opt/oracle/archredo0/foprod1/1_49508_765747965.arc
67569 1 49509 X 02-MAR-13 /opt/oracle/archredo0/foprod1/1_49509_765747965.arc
67570 1 49510 X 02-MAR-13 /opt/oracle/archredo0/foprod1/1_49510_765747965.arc
4. Re-run the log backup for check from crontab
fodbsx7.hk.ocean.local:/opt/oracle/archredo0/foprod1$ /usr/local/bin/descron "/opt/oracle/ocean_rman_backup.sh log" "Oracle Backups" logs-oracle
How to change DBID of Oracle Database
use Note: 224266.1 From Metalink
-Check DBID for
both target and source instance ( they will be same)
select dbid,
name, open_mode, activation#, created from v$database;
Command to change:
-nid target=sys/manager@TEST_DB
Command to change Password file:
--Backup password file
[orafvnd@db1001]$ mv orapwTEST orapwTEST_old
-rwSr----- 1 oratest fvndba 1536 Sep 3 17:05 orapwFVND_old
[oratest@db1001]$
orapwd file=orapwTEST password=manager entries=2
Sunday, September 20, 2015
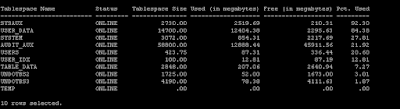
SQL query to check Tablespace Utilization in Oracle Database.
SET LINESIZE 150
SET PAGESIZE 9999
SET VERIFY OFF
COLUMN status FORMAT a9 HEADING 'Status'
COLUMN name FORMAT a25 HEADING 'Tablespace Name'
COLUMN ts_size FORMAT 999999.99 HEADING 'Tablespace Size'
COLUMN used FORMAT 999999.99 HEADING 'Used (in megabytes)'
COLUMN free FORMAT 999999.99 HEADING 'Free (in megabytes)'
COLUMN pct_used FORMAT 999.99 HEADING 'Pct. Used'
SELECT d.tablespace_name name,
d.status status,
NVL(a.bytes, 0)/1024/1024 ts_size,
NVL(a.bytes - NVL(f.bytes, 0), 0)/1024/1024 used,
NVL(f.bytes, 0)/1024/1024 free,
NVL((a.bytes - NVL(f.bytes, 0)) / a.bytes * 100, 0) pct_used
FROM sys.dba_tablespaces d,
( select tablespace_name, sum(bytes) bytes from dba_data_files group by tablespace_name) a,
( select tablespace_name, sum(bytes) bytes from dba_free_space group by tablespace_name) f
WHERE d.tablespace_name = a.tablespace_name(+)
AND d.tablespace_name = f.tablespace_name(+)
ORDER BY pct_used desc;
Sample output:
Install Oracle XE Database on Linux/Centos (Oracle Express Database Installation)
Download Oracle XE DB repository and place it in the server
[root@test linux]# ls -rlt oracle*
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 315891481 Dec 17 2013 oracle-xe-11.2.0-1.0.x86_64.rpm.zip
[root@test linux]# pwd
/var/software/linux
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 315891481 Dec 17 2013 oracle-xe-11.2.0-1.0.x86_64.rpm.zip
[root@test linux]# pwd
/var/software/linux
1. Install and Configure Centos 6.3, with required rpm packages
After installing Centos 6.3, be sure to install the following rpm packages.
□ LIBAIO: libaio-0.3.107-10.el6.x86_64.rpm
□ BC: bc-1.06.tar.gz
Connect to DB Server and log in as root
# yum install libaio bc
or
# rpm –Uvh package_name.rpm download the rpm package file if no internet access available;
Note: Type y when prompted for confirmation; Type y when prompted for warning on the GPG key. You should see the Complete!
2. Install Oracle11g XE
2.1
linux =>
(root)
groupadd dba
useradd oracle -g dba -G dba
(root)
groupadd dba
useradd oracle -g dba -G dba
2.2
Create Oracle installation folder:
# mkdir /opt/oracle
Copy oracle-xe-11.2.0-1.0.x86_64.rpm.zip to /opt/Oracle folder,
# cd /opt/oracle
# unzip oracle-xe-11.2.0-1.0.x86_64.rpm.zip;
Modify kernel parameters,
# vi /etc/sysctl.conf
add the following parameters
kernel.shmall = 2097152
kernel.shmmni = 4096
Verify the change,
# /sbin/sysctl –p
2.3
Switch to folder Disk1,
# cd Disk1
# rpm -ivh oracle-xe-11.2.0-1.0.x86_64.rpm
Centos VM may not accept some kernel parameters and just ignore the error message.
3. Configure Oracle11g XE
3.1
Configure oracle database,
# /etc/init.d/oracle-xe configure
Unless you want to change the port numbers, you only need to set the password for SYS and SYSTEM
The installation process will create directory /u01, which Oracle XE will be installed
3.2
Set required Oracle environment variables, login in as oracle,
# su - oracle
# vi /home/oracle/.bash_profile
And add the following lines after export PATH
export ORACLE_HOME=/u01/app/oracle/product/11.2.0/xe
export ORACLE_SID=XE
export ORACLE_BASE=/u01/app/oracle
export PATH=$ORACLE_HOME/bin:$PATH
LSNR=$ORACLE_HOME/bin/lsnrctl
ORACLE_OWNER=oracle
LOG="$ORACLE_HOME_LISTNER/listener.log"
Or
Add the following line to the .bashrc or .bash_profile of the users you want to access the environment:
/u01/app/oracle/product/11.2.0/xe/bin/oracle_env.sh
Test the access to Oracle database,
# sqlplus /nolog
# connect sys/password as sysdba
To allow remote access to Oracle 11g XE GUI (as well as Application Express GUI),
EXEC DBMS_XDB.SETLISTENERLOCALACCESS(FALSE);
You should now be able to access the Oracle 11g XE Home Page GUI at:
http://ip_address:8080/apex/f?p=4950:1
ip_address is your server IP and 8080 is the default listener port;
ORA-00020: maximum number of processes
How to check and resolve : ORA-00020: maximum number of processes
ps -ef|grep oracle
kill -9
select inst_id, username, machine, program, status, count(*) "Connections"
from gv$session
where username is not null
group by inst_id, username, machine, program, status
order by 1, 6 desc;
SQL> alter system set processes=700 scope=spfile sid='*';
System altered.
SQL> alter system set sessions=1072 scope=spfile sid='*';
System altered.
if Oracle RAC
[oracle@ test-db2 ~]$ srvctl stop database -d DB_NAME
[oracle@ test-db2 ~]$ srvctl start database -d DB_NAME
[oracle@ test-db2 ~]$ srvctl status database -d DB_NAME
Instance TEST1 is running on node test-db1
Instance TEST2 is running on node test-db2
1. Login into the Oracle Database and if you cannot sqlplus into it. Try killing a few oracle server processes.
ps -ef|grep oracle
kill -9
2. Try to sqlpus now, check existing sessions:
select inst_id, username, machine, program, status, count(*) "Connections"
from gv$session
where username is not null
group by inst_id, username, machine, program, status
order by 1, 6 desc;
3. Increase the number of processes and sessions
SQL> alter system set processes=700 scope=spfile sid='*';
System altered.
SQL> alter system set sessions=1072 scope=spfile sid='*';
System altered.
4. Bounce the db
if Oracle RAC
[oracle@ test-db2 ~]$ srvctl stop database -d DB_NAME
[oracle@ test-db2 ~]$ srvctl start database -d DB_NAME
[oracle@ test-db2 ~]$ srvctl status database -d DB_NAME
Instance TEST1 is running on node test-db1
Instance TEST2 is running on node test-db2
5. Verify if the parameters are increased using the below query
select * from gv$resource_limit
where resource_name in ('processes', 'sessions')
order by 2, 1;
For example:
Compiling Invalid Objects in Oracle Database
UTLRP.sh (script)
1st – sshsu ora _ _ _ _
2nd – Check to make sure
utlrp.sh script is in ORACLE_HOME
>cd
$ORACLE_HOME
>cd
rdbms/admin/utlrp.sh
3rd – logon to sqlplus (as
sysdba)
>sqlplus
‘/as sysdba’
4th – Run query to count how
many invalid objects in the instance
>
SELECT COUNT(*) "num_invalid_objects"
FROM DBA_OBJECTS
WHERE STATUS = 'INVALID'
and OWNER NOT IN ('NOETIX', 'NOETIX_SYS');
5th – Run the UTLRP script
>@utlrp
6th – Run the query to count
invalid objects again, the number must go down.
>
SELECT COUNT(*) "num_invalid_objects"
FROM DBA_OBJECTS
WHERE STATUS = 'INVALID'
and OWNER NOT IN ('NOETIX', 'NOETIX_SYS') ;
How to Add a Datafile in Oracle Database
To Check Database
-----------------
sqlplus "/as sysdba"
set pages 9999 lines 300
col OPEN_MODE for a10
col HOST_NAME for a10
select name DB_NAME,INSTANCE_NAME,HOST_NAME,OPEN_MODE,version DB_VERSION,DATABASE_STATUS,DATABASE_ROLE,PROTECTION_LEVEL,CONTROLFILE_TYPE,LOGINS,to_char(STARTUP_TIME,'DD-MON-YYYY HH24:MI:SS') "UP TIME"from v$database,gv$instance;
ASM Space Report
SET LINESIZE 150
SET PAGESIZE 9999
SET VERIFY off
COLUMN group_name FORMAT a20 HEAD 'Disk Group|Name'
COLUMN sector_size FORMAT 99,999 HEAD 'Sector|Size'
COLUMN block_size FORMAT 99,999 HEAD 'Block|Size'
COLUMN allocation_unit_size FORMAT 999,999,999 HEAD 'Allocation|Unit Size'
COLUMN state FORMAT a11 HEAD 'State'
COLUMN type FORMAT a6 HEAD 'Type'
COLUMN total_mb FORMAT 999,999,999 HEAD 'Total Size (MB)'
COLUMN used_mb FORMAT 999,999,999 HEAD 'Used Size (MB)'
COLUMN pct_used FORMAT 999.99 HEAD 'Pct. Used'
SELECT
distinct name group_name
, sector_size sector_size
, block_size block_size
, allocation_unit_size allocation_unit_size
, state state
, type type
, total_mb total_mb
, (total_mb - free_mb) used_mb
, ROUND((1- (free_mb / total_mb))*100, 2) pct_used
FROM
gv$asm_diskgroup
ORDER BY
name
/
Datafiles of a particular TableSpace
set pages 200
set lines 200
col tablespace_name for a30
col file_name for a80
select tablespace_name,file_name,bytes/1024/1024 Size_MB,autoextensible,maxbytes/1024/1024 MAXSIZE_MB from dba_data_files where tablespace_name='&TABLESPACE_NAME' order by 1,2;
All schema object details in a tablespace
set pages 9999 lines 300
col tablespace_name format a15
col segment_name format a40
col segment_type format a20
col PARTITION_NAME format a20
col mb format 999,999,999
select owner
, tablespace_name
, segment_name
, segment_type
, PARTITION_NAME
, ceil(sum(bytes) / 1024 / 1024) "Size in MB"
from dba_segments
where tablespace_name like '&tablespace_name'
group by segment_name
order by ceil(sum(bytes) / 1024 / 1024) desc
/
TABLESPACE DDL
set pagesize 0
SET LONG 9999999
select dbms_metadata.get_ddl('TABLESPACE','&TABLESPACE_NAME') FROM DUAL;
To resize a datafile (ASM)
ALTER DATABASE DATAFILE '&FILE_NAME' RESIZE 4096M;
ALTER DATABASE DATAFILE '&FILE_NAME' AUTOEXTEND ON MAXSIZE 8G;
To add a new datafile in a tablespace (ASM)
BEFORE ADDING A DATAFILE WE SHOULD CHECK FOR DUPLICATE DATAFILE For datafile
select tablespace_name,file_name from dba_data_files where file_name like '%&datafilename%';
ALTER TABLESPACE ADD DATAFILE '+DATA' SIZE 100M AUTOEXTEND ON NEXT 100M MAXSIZE UNLIMITED;
To Create a new tablespace (ASM)
CREATE TABLESPACE DATAFILE '+DATA' SIZE 100M AUTOEXTEND ON NEXT 100M MAXSIZE UNLIMITED;
Schemas in a tablespace
set pages 999
col "size MB" format 999,999,999
col "Objects" format 999,999,999
select obj.owner "Owner"
, obj_cnt "Objects"
, decode(seg_size, NULL, 0, seg_size) "size MB"
from (select owner, count(*) obj_cnt from dba_objects group by owner) obj
, (select owner, ceil(sum(bytes)/1024/1024) seg_size
from dba_segments group by owner) seg
where obj.owner = seg.owner
set pages 9999 lines 300
col OPEN_MODE for a10
col HOST_NAME for a10
select name DB_NAME,INSTANCE_NAME,HOST_NAME,OPEN_MODE,version DB_VERSION,DATABASE_STATUS,DATABASE_ROLE,PROTECTION_LEVEL,CONTROLFILE_TYPE,LOGINS,to_char(STARTUP_TIME,'DD-MON-YYYY HH24:MI:SS') "UP TIME"from v$database,gv$instance;
ASM Space Report
----------------
SET LINESIZE 150SET PAGESIZE 9999
SET VERIFY off
COLUMN group_name FORMAT a20 HEAD 'Disk Group|Name'
COLUMN sector_size FORMAT 99,999 HEAD 'Sector|Size'
COLUMN block_size FORMAT 99,999 HEAD 'Block|Size'
COLUMN allocation_unit_size FORMAT 999,999,999 HEAD 'Allocation|Unit Size'
COLUMN state FORMAT a11 HEAD 'State'
COLUMN type FORMAT a6 HEAD 'Type'
COLUMN total_mb FORMAT 999,999,999 HEAD 'Total Size (MB)'
COLUMN used_mb FORMAT 999,999,999 HEAD 'Used Size (MB)'
COLUMN pct_used FORMAT 999.99 HEAD 'Pct. Used'
SELECT
distinct name group_name
, sector_size sector_size
, block_size block_size
, allocation_unit_size allocation_unit_size
, state state
, type type
, total_mb total_mb
, (total_mb - free_mb) used_mb
, ROUND((1- (free_mb / total_mb))*100, 2) pct_used
FROM
gv$asm_diskgroup
ORDER BY
name
/
Datafiles of a particular TableSpace
------------------------------------
set pages 200set lines 200
col tablespace_name for a30
col file_name for a80
select tablespace_name,file_name,bytes/1024/1024 Size_MB,autoextensible,maxbytes/1024/1024 MAXSIZE_MB from dba_data_files where tablespace_name='&TABLESPACE_NAME' order by 1,2;
All schema object details in a tablespace
-----------------------------------------
set pages 9999 lines 300col tablespace_name format a15
col segment_name format a40
col segment_type format a20
col PARTITION_NAME format a20
col mb format 999,999,999
select owner
, tablespace_name
, segment_name
, segment_type
, PARTITION_NAME
, ceil(sum(bytes) / 1024 / 1024) "Size in MB"
from dba_segments
where tablespace_name like '&tablespace_name'
group by segment_name
order by ceil(sum(bytes) / 1024 / 1024) desc
/
TABLESPACE DDL
--------------
set pagesize 0SET LONG 9999999
select dbms_metadata.get_ddl('TABLESPACE','&TABLESPACE_NAME') FROM DUAL;
To resize a datafile (ASM)
---------------------------
ALTER DATABASE DATAFILE '&FILE_NAME' RESIZE 4096M;ALTER DATABASE DATAFILE '&FILE_NAME' AUTOEXTEND ON MAXSIZE 8G;
To add a new datafile in a tablespace (ASM)
--------------------------------------------
BEFORE ADDING A DATAFILE WE SHOULD CHECK FOR DUPLICATE DATAFILE For datafile
select tablespace_name,file_name from dba_data_files where file_name like '%&datafilename%';
ALTER TABLESPACE
To Create a new tablespace (ASM)
---------------------------------
CREATE TABLESPACE
Schemas in a tablespace
-----------------------
set pages 999col "size MB" format 999,999,999
col "Objects" format 999,999,999
select obj.owner "Owner"
, obj_cnt "Objects"
, decode(seg_size, NULL, 0, seg_size) "size MB"
from (select owner, count(*) obj_cnt from dba_objects group by owner) obj
, (select owner, ceil(sum(bytes)/1024/1024) seg_size
from dba_segments group by owner) seg
where obj.owner = seg.owner
Creating tablespace in Oracle Database
Creating tablespace (for datafiles tablespace name ends with D and for index files ends
with X)
Log into sqlplus (as sysdba)
>create tablespace datafile ‘dir…..dbf’ size 10M autoextend on next 10M maxsize 2000M
uniformsize;
Creating Users in Oracle
Log into sqlplus (as sysdba)
>create user
identified by default tablespace
temporary tablespace TEMP quota unlimited on quota untitled on
>grant connect to ;
>grant resource to ;
Check Patchset Level
Log in as an app user
Check for adutconf.sql file
>cd $AD_TOP/sql/adutconf.sql
>sqlplus
>@adutconf
Should create adutconf.lst file or
()
Applying Patches using adpatch
**********************
Steps overview:
**********************
**********************
- bring down instance
- Enable Maintenance mode
- Apply Patch
- Disable Maintenance
**********************
Steps in detail:
**********************
Steps in detail:
**********************
1st –Research patch (check
prereqs and settings)
2nd- check that it hasn’t been
applied already
SQL>
select * from ad_bugs where bug_number = ‘’;
3rd – FTP the patch from oracle
>ftp
updates.oracle.com (coresys/coredba)
>cd
>bin
>
ls – ex. ls –linux
>get
.zip ex. get
p3948369_11i_linux.zip
>bye
4th – go the patch directory
>cd
/patch/patches or solaris or generic
5th - unzip the patch in
/patch/patches/SOLARIS/XXXX/
6th - bring down the instance and email everyone(opsdesk,
dbadesk and functional)
-Run
the shut script in home directory
-
Make sure all processes are dead
7th – go to adpatch (all defaults
except size = 12,000 and sys pwd = manager)
Apply
patches in order (‘c,d,g’ in that order – or just ‘u’ if only one)
(“adpatch flags=hidepw options=noprereq” if
it doesn’t work successfully? Only sometimes?)
Here are the prompts you will get, step by
step:
- Is this the correct APPL_TOP [Yes] ?
- Filename [adpatch.log] : XXXX_c/d/g/u#.log, i.e. - INST_c3358343.log
- You can be notified by email if a failure
occurs.
Do you wish to activate this feature [No] ?
- Please enter the batchsize [1000] : 12000
- Is this the correct database [Yes] ?
- Enter the password for your 'SYSTEM'
ORACLE schema: manager
- Enter the ORACLE password of Application
Object Library [APPS] : - sometimes apps
- The default directory is [/patch/patches/SOLARIS/INTT/3358343]
:
- Please enter the name of your AutoPatch
driver file - c/d/g#.drv i.e. - d3358343.drv
ON d DRIVERS:
AD utilities can support a maximum of 999
workers. Your
current database configuration supports a
maximum of 222 workers.
Oracle recommends that you use between 20
and 40 workers.
Enter the number of parallel workers [20] :
Watch it go!
*
* if error occurs asking to change the maintenance mode- change mode using
adadmin
and re-run the patch and press no to the question asking to start
where
patch last left of and then yes to confirm answer. Once the patch is
done-
go back to adadmin and disable maintenance mode.
8th – bring up the instance : start
9th – bounce apache server
-
log into application and submit active users before releasing the instance.
10th – compile invalid objects
after patching
11th - run the above query and
check file version to make sure patch has been applied.
Enabling SQL Trace in Oracle Database
The SQL Trace facility can either be enabled/disabled for an individual
session or the instance.
* To enable the SQL trace facility for your session
issue the following SQL statement:
ALTER SESSION
SET SQL_TRACE = TRUE;
* To disable the SQL trace facility for your session
issue the following SQL statement:
ALTER SESSION
SET SQL_TRACE = FALSE;
To find out if instance is in AutoConfig mode or not?
Log in as appl _ _ _ _.
>cd $APPL_TOP/admin
>ls *.xml (should have SID.xml files)
- If there is .xml file than (it usually is in auto-config mode) but check the time stamp
- If sid.xml is NOT there than its not in auto-config mode
Check Oracle Database Status (RAC or Standalone)
SQL PLUS into the database and then run the below query
set echo off
set line 150
set pages 100
set serveroutput on
set feedback on
set time on
set timing on
col HOST_NAME for a30
col "UP TIME" for a25
show user
select name,INSTANCE_NAME,OPEN_MODE,HOST_NAME,DATABASE_STATUS,logins,to_char(STARTUP_TIME,'DD-MON-YYYY HH24:MI:SS') "UP TIME"from v$database,v$instance;
select instance_name,HOST_NAME from gv$instance order by 1;
col "Datafiles Status" for a40
select distinct status "Datafiles Status" from v$datafile;
set echo on
set line 150
set pages 100
set serveroutput on
set feedback on
set time on
set timing on
col HOST_NAME for a30
col "UP TIME" for a25
show user
select name,INSTANCE_NAME,OPEN_MODE,HOST_NAME,DATABASE_STATUS,logins,to_char(STARTUP_TIME,'DD-MON-YYYY HH24:MI:SS') "UP TIME"from v$database,v$instance;
select instance_name,HOST_NAME from gv$instance order by 1;
col "Datafiles Status" for a40
select distinct status "Datafiles Status" from v$datafile;
set echo on
Wednesday, August 12, 2015
Change Oracle Wallet Keys
1. Backup the current P12 to archive
a. Oracle Wallet keys are stored in ACFS, a cluster file system on top of ASM. On Unix, access to the wallet is be limited to the 'oracle:oinstall' user:group, using proper directory (700) and file permissions (600).
b. Its back up after each master-rekey operation or changes to a encrypted network drive. (Kee-Pass)
c. The backups are stored away from database backups.
2. Use orapki wallet display -wallet to see master key list and validate the password
[TEST-DB]/ora/wallets/test-db> orapki wallet display -wallet /ora/wallets/test-db/
Oracle PKI Tool : Version 11.2.0.3.0 - Production
Copyright (c) 2004, 2011, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Enter wallet password:
Requested Certificates:
User Certificates:
Oracle Secret Store entries:
oracle.security.client.connect_string1
oracle.security.client.password1
oracle.security.client.username1
ORACLE.SECURITY.DB.ENCRYPTION.
ORACLE.SECURITY.DB.ENCRYPTION.
ORACLE.SECURITY.DB.ENCRYPTION.
ORACLE.SECURITY.DB.ENCRYPTION.MASTERKEY
Trusted Certificates:
Subject: OU=Class 1 Public Primary Certification Authority,O=VeriSign\, Inc.,C=US
Subject: OU=Class 3 Public Primary Certification Authority,O=VeriSign\, Inc.,C=US
Subject: OU=Class 2 Public Primary Certification Authority,O=VeriSign\, Inc.,C=US
Subject: OU=Secure Server Certification Authority,O=RSA Data Security\, Inc.,C=US
Subject: CN=GTE CyberTrust Global Root,OU=GTE CyberTrust Solutions\, Inc.,O=GTE Corporation,C=US
3. Change Oracle Wallet Password
[test-db1]/ora/wallets/test-db> orapki wallet change_pwd -wallet /ora/wallets/test-db/
Oracle PKI Tool : Version 11.2.0.3.0 - Production
Copyright (c) 2004, 2011, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Enter wallet password:
New password:
Enter wallet password:
[test-db1]/ora/wallets/test-db>
4. Use orapki wallet display -wallet to see that a new master key has been added
[test-db1]/ora/wallets/test-db/client> orapki wallet display -wallet /ora/wallets/test-db/
Oracle PKI Tool : Version 11.2.0.3.0 - Production
Copyright (c) 2004, 2011, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Enter wallet password:
PKI-02002: Unable to open the wallet. Check password.
[test-db1]/ora/wallets/test-db/client> orapki wallet display -wallet /ora/wallets/test-db/
Oracle PKI Tool : Version 11.2.0.3.0 - Production
Copyright (c) 2004, 2011, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Enter wallet password:
Requested Certificates:
User Certificates:
Oracle Secret Store entries:
oracle.security.client.connect_string1
oracle.security.client.password1
oracle.security.client.username1
ORACLE.SECURITY.DB.ENCRYPTION.
ORACLE.SECURITY.DB.ENCRYPTION.
ORACLE.SECURITY.DB.ENCRYPTION.
ORACLE.SECURITY.DB.ENCRYPTION.MASTERKEY
Trusted Certificates:
Subject: OU=Class 1 Public Primary Certification Authority,O=VeriSign\, Inc.,C=US
Subject: OU=Class 3 Public Primary Certification Authority,O=VeriSign\, Inc.,C=US
Subject: OU=Class 2 Public Primary Certification Authority,O=VeriSign\, Inc.,C=US
Subject: OU=Secure Server Certification Authority,O=RSA Data Security\, Inc.,C=US
Subject: CN=GTE CyberTrust Global Root,OU=GTE CyberTrust Solutions\, Inc.,O=GTE Corporation,C=US
[test-db1]/ora/wallets/test-db/client>
5. Backup the new P12 to archive and the Kee-Pass
6. Close the wallet and reopen
SQL> alter system set encryption wallet open identified by "";
alter system set encryption wallet open identified by ""
*
ERROR at line 1:
ORA-28353: failed to open wallet
SQL> alter system set encryption wallet open identified by "";
System altered.
SQL> exit
7. Run a query that touches TDE encrypted data
--When the wallet is closed
select * from encrypted_table;
ORA-28365: wallet is not open
28365. 0000 - "wallet is not open"
*Cause: The security module wallet has not been opened.
*Action: Open the wallet.
--Opening the wallet
select count(*) from encrypted_table;
17981
Tuesday, August 11, 2015
Generate DDL of Oracle Schema Using Expdp
1. Login to Oracle db
expdp "'"/ as sysdba"'" schemas=schema_name1,schema_name2 dumpfile=dumpfile.dmp content=METADATA_ONLY LOGFILE=expdp.log
2. Use sqlfile option with impdp
impdp "'"/ as sysdba"'" dumpfile=dumpfile.dmp sqlfile=ddl.sql
3. The output ddl.sql will contain the schema DDL of the mentioned schemas.
Relink Oracle Home and Grid Home after OS upgrade in Oracle RAC
1. Shutdown Oracle RAC crs and asm. Node wise if needed for zero downtime.
2. Perform OS Upgrade.
3. Upgrade ASMlib
Download from here.
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/server-storage/linux/downloads/rhel5-084877.html
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/topics/linux/asmlib/index-101839.html
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/server-storage/linux/asmlib/ol6-1709075.html
# rpm -Uvh oracleasm-support-xxx
# rpm -Uvh oracleasm-2.6.xxx
# rpm -Uvh oracleasmlib-xxx
# /etc/init.d/oracleasm enable
# /etc/init.d/oracleasm listdisks
4. Relink RDBMS ORACLE_HOME Binary
Use oracle
$ /bin/relink all
5. Relink grid home Binary
Note: complete full steps in onde node, then proceed to next
As UNIX/Linux “root”:
# cd /u01/app/11.2.0/grid/crs/install
# ./rootcrs.pl -unlock
Use oracle
$ cd /bin
$ ./relink all
Use root
# cd /rdbms/install
# ./rootadd_rdbms.sh
# cd /crs/install
# ./rootcrs.pl -patch
6. -- Check Log location
[grid@test-db]$ pwd
/u01/app/11.2.0/grid/log/test-db
7. Startup CRS nodewise using root
# /bin/crsctl start crs
Start the database instance if needed.
--Startup one node instance
srvctl start instance -d DB_NAME -i INST_NAME
Check if the instances are online.
$ crsctl stat res -t
++++++++++++++++++
References
++++++++++++++++++
How to Check Whether Oracle Binary/Instance is RAC Enabled and Relink Oracle Binary in RAC (Doc ID 284785.1)
Shutdown and Startup one Oracle Rac Node
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Shutdown one node:
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++
--Shutdown Instance
srvctl stop instance -d DB_NAME -i INST_NAME -o transactional
--Login as Root and shutdown crs
[root@test-db ~]# cd /u01/app/11.2.0/grid/bin
[root@test-db bin]# ./crsctl stat res -t
[root@test-db bin]# ./crsctl stop crs
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Startup one node:
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++
--Login as Root and start crs
[root@test-db ~]# cd /u01/app/11.2.0/grid/bin
crsctl start crs
crsctl check crs
--Startup one node instance
srvctl start instance -d DB_NAME -i INST_NAME
Shutdown one node:
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++
--Shutdown Instance
srvctl stop instance -d DB_NAME -i INST_NAME -o transactional
--Login as Root and shutdown crs
[root@test-db ~]# cd /u01/app/11.2.0/grid/bin
[root@test-db bin]# ./crsctl stat res -t
[root@test-db bin]# ./crsctl stop crs
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Startup one node:
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++
--Login as Root and start crs
[root@test-db ~]# cd /u01/app/11.2.0/grid/bin
crsctl start crs
crsctl check crs
--Startup one node instance
srvctl start instance -d DB_NAME -i INST_NAME
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)